Femoral Condyle | Articular Cartilage Injury
Understanding Femoral Condyles and Their Treatment
Anatomy of Femoral Condyles:
The femoral condyles, situated at the end of the thigh bone or femur, act as vital shock absorbers for the knee joint. Covered by articular cartilage, they play a crucial role in knee function and stability.
Chondromalacia in Femoral Condyles
Damage to the cartilage on the femoral condyles is commonly referred to as arthritis or chondromalacia. This condition can cause pain and discomfort in the knee joint, affecting mobility and quality of life.
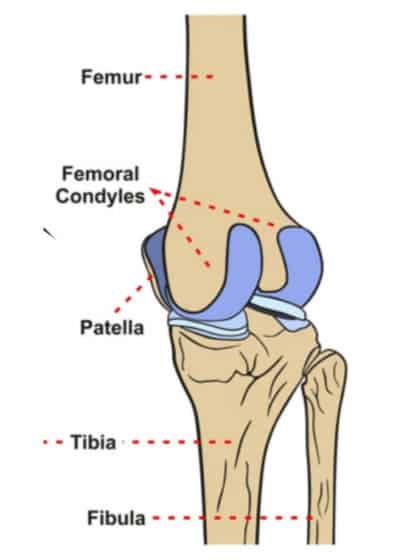
Location and Function
There are two femoral condyles: the medial condyle, located on the inside part of the knee, and the larger lateral condyle, positioned on the outside part of the knee. These condyles articulate with the tibia, specifically with the medial and lateral tibial plateaus and menisci, contributing to knee movement and stability.
Treatment Options
Various treatment options are available for cartilage damage in the femoral condyles. Conservative approaches include physical therapy to strengthen muscles and reduce stress on the knee, as well as injections of biologic agents or corticosteroids to alleviate pain and inflammation.
Chondroplasty
In cases where the cartilage defect is localized, surgical intervention like chondroplasty may be necessary. This procedure involves smoothing out rough cartilage edges to relieve mechanical irritation. While chondroplasty doesn’t cure cartilage problems, it can provide symptomatic relief in some patients.
Cartilage Replacement Surgery
For more extensive cartilage defects, cartilage replacement surgeries may be considered. These procedures aim to restore cartilage function and joint health. Options include microfracture, osteochondral transfer, and osteoarticular allograft, with the latter being the gold standard for larger defects.
Considerations for Treatment
Treatment decisions should be based on a thorough evaluation of the patient’s symptoms and overall knee health. Incidental findings on MRI may not always require intervention, and close monitoring may be sufficient in some cases. It’s crucial to prioritize patient symptoms and functional impairment when considering surgical options to ensure the best possible outcomes.
Are you suffering from Femoral Condyle Articular Cartilage Injury
There are two ways to initiate a consultation with Dr. Ravi Teja Rudraraju
You can provide current X-rays and/or MRIs for a clinical case review with with Dr. Ravi Teja Rudraraju
You can schedule an office consultation with Dr. Ravi Teja Rudraraju
Conclusion
Femoral condyle cartilage defects require careful assessment and personalized treatment plans. By considering the patient’s symptoms and overall knee health, healthcare providers can determine the most appropriate course of action to alleviate pain, improve function, and preserve joint integrity.
Latest Post

